Mekelle, Tigray – January 25, 2025 (Tigray Herald)
Arbitrary Deprivation of Life and Other Unlawful or Politically Motivated Killings in Ethiopia
There were numerous reports that the government and its representatives committed arbitrary and unlawful killings. Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch (HRW), and the UN Office of the High Commission for Human Rights (OHCHR) in collaboration with the Ethiopian Human Rights Commission (EHRC) reported numerous cases of unlawful or extrajudicial killings in the context of the conflict in Tigray and the northern part of the country (see section 1.g.). The Federal Police Internal Investigative Bureau investigated cases of criminal acts perpetrated by police. The internal unit’s decisions regarding penalties against police were kept confidential.
The Ethiopian National Defence Force (ENDF) had a military police division with a military investigative unit that reported to the military attorney general’s office. The military police passed evidence from their investigations to the prosecutors and Défense counsels. The ENDF attorney general directed the investigations and heard the cases in military court.
Unnamed groups of ethnic Gumuz militants reportedly carried out attacks and killings of civilians in various part of Benishangul-Gumuz throughout the year. Local militia groups in Afar and Somali Regions reportedly carried out attacks and killings of civilians as part of a long-running regional boundary dispute in the northeast of the country. The Oromo Liberation Army (OLA)-Shane – an armed separatist group with factions in western, central, and southern Oromia – reportedly killed civilians and government officials in many parts of Oromia, especially in the west.
Disappearance
There were reports of disappearances by or on behalf of government authorities.
On August 18, HRW reported that since late June authorities had forcibly disappeared ethnic Tigrayans in Addis Ababa. While lawyers and families discovered that the government transferred some individuals to detention centers in Afar, the whereabouts of others – including 23 cases HRW documented – remained unknown as of early August. A lawyer shared with HRW a list of an additional 110 persons whose relatives said their whereabouts were unknown as of August 2. HRW reported that several disappeared individuals had been released and re-arrested as of early December.
On September 13, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights stated reports suggested, “people of Tigrayan ethnicity have been profiled and detained by law enforcement officials on ethnic grounds, with hundreds having reportedly been arrested in recent security sweeps, mostly in Addis Ababa, and several businesses belonging to ethnic Tigrayans having reportedly been closed.”
In early November the BBC, CNN, and other news agencies reported on widespread detentions of ethnic Tigrayans in Addis Ababa and throughout the country; such reports continued at year’s end.
On November 8, the EHRC reported authorities appeared to be arresting persons “based on ethnicity” under a nationwide state of emergency declaration, which gave them power to detain “people suspected of collaborating with terrorist groups on reasonable grounds.”
In early December East Africa regional representatives for OHCHR estimated security forces had detained between 5,000 and 7,000 individuals since the government declared the state of emergency on November 2, noting this information was based on preliminary information and likely an underestimate. There were also reports of widespread disappearances on the basis on ethnicity in Western Tigray (see section
Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment
Although the constitution prohibits such practices, there were reports that security officials tortured and otherwise abused detainees.
The World Organization Against Torture and its partner the Association for Human Rights in Ethiopia reported that the government reintroduced torture in its security operations connected to the armed conflict in the northern part of the country and failed to hold soldiers accused of torture accountable (see section 1.g.).
During an EHRC investigation in Oromia early in the year, detainees reported police beat them during arrests and in detention. The EHRC’s monitoring teams found evidence of injuries on some detainees who reported police beatings.
According to the Conduct in UN Field Missions online portal, there were two open allegations of sexual exploitation and abuse by the country’s peacekeepers deployed to a UN peacekeeping mission: one submitted in 2018 allegedly involving an exploitative relationship with an adult in the UN Mission in Liberia and one submitted in late 2020 allegedly involving transactional sex in the UN Interim Security Force in Abyei. As of October the United Nations had substantiated the 2018 allegation and repatriated the perpetrator, but the government had not yet reported regarding accountability measures taken. Concerning the 2020 allegation, the United Nations had taken an interim action (suspension of payments), but results of the investigation remained pending, as was any final action.
Impunity remained a problem, although some measures were taken to hold security forces accountable for human rights abuses. Lack of transparency regarding those being charged and tried in courts of law made it difficult to assess the government’s accountability efforts. In May the federal attorney general’s office released a summary report of its efforts to ensure accountability regarding violations of national and international law in Tigray. Government investigators examined allegations that members of the ENDF engaged in killing of civilians, rape, and other forms of gender-based violence and looting and destruction of property. Military prosecutors charged 28 soldiers for killing civilians without military necessity, and 25 soldiers for committing acts of sexual violence including rape. As of year’s end trials were underway. In addition, three soldiers were convicted and sentenced for rape, and one soldier was convicted and sentenced for killing a civilian. At year’s end the military police were also investigating several other cases of alleged conflict-related crimes. Human rights groups criticized the military’s accountability efforts for lacking transparency.
Prison and Detention Center Conditions
Prison and pretrial detention center conditions remained harsh and in some cases life threatening. Problems included gross overcrowding and inadequate food, water, sanitation, and medical care. Pretrial detention often occurred in police station detention facilities, where conditions varied widely, and reports noted poor hygiene.
Beginning in early November, according to media reports, the government began detaining thousands of ethnic Tigrayans under its state of emergency, converting warehouses, schools, youth centers, and other makeshift facilities to house the ever-growing detainee population. The conditions in such facilities were reportedly life threatening (see sections 1.b. and 1.d.).
Physical Conditions: Severe overcrowding was common, especially in prison sleeping quarters. The nongovernmental organization (NGO) World Prison Brief estimated the country’s prisons held 110,000 persons in March 2020, although they had no estimate of the prison system’s capacity. Prison cells were small and cramped. International organizations reported it was common for cells to have small windows that allowed only a little light into estimated 430-square-foot cells, one of which might hold as many as 38 cellmates. Authorities sometimes incarcerated juveniles with adults. Prison officials generally separated male and female prisoners, although mixing occurred at some facilities. Authorities did not provide information on deaths in prison.
Many prisoners supplemented their food allocation with daily food deliveries from family members or by purchasing food from local vendors. Reports noted officials prevented some prisoners from receiving food from their families, and some families did not know of their relatives’ locations. Medical care was unreliable in federal prisons and almost nonexistent in regional ones. Medical attention following physical abuse was insufficient in some cases.
Prisoners had only limited access to potable water. Water shortages caused unhygienic conditions, and most prisons lacked appropriate sanitary facilities. Many prisoners had serious health problems but received little or no treatment. There were reports prison officials denied some prisoners access to needed medical care.
The law prohibits detention in any facility other than an official detention center; however, local militias and other formal and informal law enforcement entities operated an unknown number of unofficial detention centers.
Most prisons and detention centers lacked adequate hand-washing facilities, personal protective equipment, and quarantine areas. As a result the prison system was vulnerable to the spread of COVID-19. To reduce crowding and slow the spread of COVID-19, the government released 30,000 prisoners from the federal prison system.
Administration: There were reports that prisoners were mistreated by prison guards and did not have access to prison administrators or ombudspersons to register their complaints. Legal aid clinics operated in some prisons. At the regional level, these clinics had good working relations with judicial, prison, and other government officials. Prison officials allowed some detainees to submit complaints to judicial authorities without censorship, but courts sometimes declined to hear such complaints.
The law generally provides for visitor access to prisoners. Authorities, however, denied some indicted defendants visits with their lawyers. In some cases police did not allow pretrial detainees to have access to visitors, including family members and legal counsel. Prison regulations stipulate lawyers representing persons charged with terrorism offenses may visit only one client per day, and only on Wednesdays and Fridays. Authorities denied family members’ access to persons charged with terrorist activity.
Officials permitted religious observance by prisoners, but this varied by prison and even by section within a prison. There were allegations authorities denied detainees adequate locations in which to pray.
Independent Monitoring:
From January to June, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) visited 17,919 prisoners in 32 places of detention throughout the country as part of its normal activities. After the government commenced its widespread detention of ethnic Tigrayans under the state of emergency (see section 1.d.), the ICRC was denied access to detention facilities.
Regional authorities allowed government and NGO representatives to meet with prisoners without third parties present. The EHRC monitored federal and regional detention centers and interviewed prison officials and prisoners.
During the period from November 20, 2020, to January 12, the EHRC deployed monitoring teams at 21 police stations across Oromia where large numbers of prisoners were arrested and detained in connection with what local authorities called “the current situation,” referring to unrest following the killing of popular singer Hachalu Hundessa. Detainees also reported extortion practices by police. In most police stations the EHRC observed, detainees were held in unhygienic and overcrowded rooms that posed serious health risks. The EHRC reported that most detainees faced dire conditions due to absence of food in the detention centers coupled with lack of access to water, sanitation, and medical services.
The EHRC and the attorney general’s office checked on the welfare of high-level political prisoners arrested for possible involvement in organizing violence following the June 2020 killing of popular singer Hachalu Hundessa. On February 2, the EHRC visited Kaliti Correctional Facility and Kilinto Prison to monitor the situation of Jawar Mohammed and other prisoners who had been on hunger strike that began on January 27, as well as the treatment of Colonel Gemechu Ayana and Tilahun Yami. The EHRC reported the detainees were in good health, had sustained no bodily injuries, and that those on hunger strike were subject to medical monitoring.
The constitution and federal law prohibit arbitrary arrest and detention and provide for the right of any person to challenge the lawfulness of his or her arrest or detention in court. The government rarely observed these requirements, especially regarding the mass detentions made under the state of emergency (see section 1.b.).
The law provides for an independent judiciary. Although the civil courts operated with a large degree of independence, criminal courts remained weak and overburdened.
The law generally requires authorities to obtain court-issued search warrants prior to searching private property, although the government did not always enforce this, especially under the state of emergency imposed in November.
The law also recognizes exceptions for “hot pursuit” cases in which a suspect enters premises or disposes of items that are the subject of an offense committed on the premises. This legal exception also applies when police have reasonable suspicion that evidence of a crime punishable if convicted by more than three years’ imprisonment is concealed on or in the property and a delay in obtaining a search warrant could allow for the evidence to be removed. Freedom House reported the government used location tracking and other technical means to surveil online and telephone communications. In addition, the government blocked or filtered websites for political reasons, and there was reportedly no mechanism to appeal website blocking.
Beginning in November 2020, fighting between the ENDF and TPLF resulted in protracted conflict throughout the northern area of Tigray Region. During the year the conflict spread into neighboring Amhara and Afar Regions, where serious abuses were also reported. As of year’s end there was very limited access to Tigray, except for the capital Mekele, resulting in a lack of reporting on human rights abuses in Tigray. There were numerous reports of looting and destruction of infrastructure in Tigray, Amhara, and Afar, including in refugee camps. There were reports that government security forces, regional security forces, the Eritrean Defense Forces (EDF), private militias, and the TPLF all committed human rights abuses.
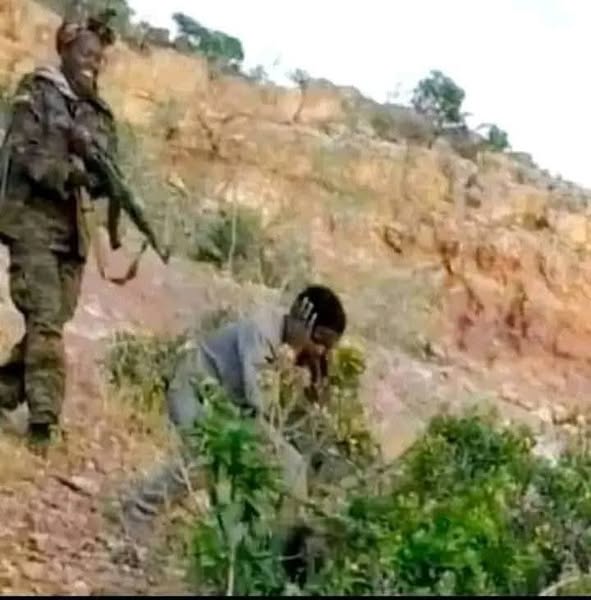
Killings: There were widespread reports that government security forces killed civilians in the context of the continuing conflict in the northern part of the country. Reports of regional militias, EDF, and rebel groups killing civilians in the context of the conflict were likewise widespread.
In early and mid-January, local and international media reported that the ENDF killed at least 30 civilians in Mai Harmaz in western Tigray and at least 11 civilians in Mahibere Dego in central Tigray. Media also reported that on or about February 11, ENDF soldiers killed 18 civilians in Wikro in eastern Tigray Region. Staff from Medecins Sans Frontieres reported witnessing ENDF soldiers kill four civilians in Adigrat, Tigray, in March. On April 9, a partner organization of the NGO-operated Armed Conflict Location and Event Database Project reported that ENDF soldiers killed at least 33 civilians in Selekleka in northern Tigray.
In August multiple news agencies, including Agence France-Presse, the New York Times, the Associated Press, and CNN, did feature stories regarding the bodies of what appeared to be executed Tigrayans being found in the town Wad al-Hilou, Sudan, which is 40 miles along the Tekeze River from Humera, Ethiopia. On September 13, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights stated, “We have received disturbing reports that local fishermen found dozens of bodies floating along the river crossing between Western Tigray and Sudan in July. Some allegedly had gunshot wounds and bound hands, indications that they might have been detained and tortured before being killed.” CNN reported that many of the bodies bore marks of “extensive torture.” One CNN witness had counted 60 bodies to date. According to CNN, the bodies were believed to be the remains of Tigrayans incarcerated in Humera by the ENDF and associated militia groups. According to a Sudanese forensic expert who identified some of the bodies, “We found clear signs of a systematic manner of torture – aggressive and painful violence with intent to kill. The victims were dead before they hit the water.”
According to a mid-December Amnesty International and HRW report, Amhara security forces were responsible for a surge of mass detentions, killings, and forced expulsions of ethnic Tigrayans in Western Tigray. Earlier that month HRW reported Tigrayan forces had executed dozens of civilians in two towns they temporarily controlled in Amhara Region. According to the November 3 OHCHR-EHRC report, there were reasonable grounds to believe all parties to the conflict – including the ENDF, EDF, and TPLF – carried out indiscriminate attacks resulting in civilian casualties and destruction or damage to civilian objects. According to reports by the Guardian, New York Times, Washington Post, CNN, al-Jazeera, SkyNews, and others, on June 22, government forces bombed a marketplace in Togogo, Tigray Region, killing dozens of civilians. Medical personnel told Reuters the ENDF blocked them from reaching the site of the attack.
Abductions: According to the November 3 OHCHR-EHRC report, the ENDF detained individuals in secret locations and military camps, in many cases arbitrarily. The TPLF and groups allied to them reportedly arbitrarily detained and abducted non-Tigrayan civilians some of whom were killed or disappeared.
Physical Abuse, Punishment, and Torture:According to the November 3 OHCHR-EHRC report, all parties to the conflict engaged in torture and ill-treatment of civilians and captured combatants. Victims were reportedly beaten with electric cables and metal pipes, detained incommunicado, threatened with guns to their heads, and deprived of food and water. Civilians in Western Tigray were reportedly tortured and ill-treated mainly because of their ethnic identities as Amhara. Elsewhere, captured soldiers and fighters, as well as civilians suspected of providing support to them, were reportedly tortured. According to the OHCHR-EHRC report, on April 2, in Samre, EDF soldiers forcibly paraded at least 600 Tigrayan men, who were stripped to their underpants or naked, through the town. The report detailed how the TPLF also subjected captured ENDF soldiers to public view.
Reports were widespread that parties to the conflict in the northern part of the country used rape as a weapon of war, with numerous allegations against the ENDF, EDF, and Amhara Regional Special Forces and associated militia groups. Amnesty International documented 1,288 cases of sexual violence attributed to government forces between February and April. In February the Ministry of Women, Children, and Youth recognized the widespread use of rape in Tigray, establishing a task force to investigate allegations and send a report to the Attorney General’s Office. Women and girls in Tigray reported to local and international media that men in Ethiopian military uniforms subjected them to rape, gang rape, sexual slavery, sexual mutilation, sexual exploitation and abuse, and other forms of gender-based violence. Survivors reported that pregnant women, women with disabilities, and young girls were targeted, and that in some cases rapists used ethnic slurs. One woman reported to Reuters that men dressed in Ethiopian military uniforms killed her 12-year-old son in Mekelle, then took her to a camp where she was held with other female captives and repeatedly raped for 10 days in mid- to late-February. In other similar reports survivors reported difficulty distinguishing whether their abusers were Ethiopian soldiers or Eritreans wearing Ethiopian uniforms. According to the OHCHR-EHRC report, there were reasonable grounds to believe that all parties to the conflict committed sexual and gender-based violence, with the ENDF, EDF, and TPLF implicated in multiple reports of gang rape. A November 9 report by Amnesty International documented more than a dozen reports of rapes committed by TPLF fighters.
In June the Attorney General’s Office stated that the court convicted four ENDF soldiers of rape, and that 21 additional suspects had been charged with committing acts of sexual violence and rape.
Child Soldiers:There were some reports of conscription and use of child soldiers by government forces and armed groups.
In August Tigrayan teenagers reported to the BBC that the TPLF had been forcibly conscripting child soldiers. Since June the government accused the TPLF of using child soldiers, but the TPLF spokesperson denied the allegations.
On September 29, local media reported that authorities in the Borana Zone in southern Oromia were forcibly conscripting youth to join the ENDF. Local officials dismissed these reports as propaganda.
Other Conflict-related Abuse: In the context of the conflict in the northern part of the country, international organizations, including the United Nations, reported that a humanitarian crisis, including man-made widespread famine was unfolding and sought to assist with basic services, food, and medical supplies. The government, however, significantly impeded or blocked access to areas in need of humanitarian assistance, especially in Tigray. In June the UN’s top humanitarian official, Mark Lowcock, stated that soldiers were deliberately blocking supplies to the more than one million persons in areas outside of government control and told Reuters, “Food is definitely being used as a weapon of war.” On October 8, the NGO InterAction noted the use of “starvation as warfare.”
According to the November 3 OHCHR-EHRC report, there were reasonable grounds to believe all parties to the conflict – including the ENDF, EDF and TPLF – either directly attacked civilians and civilian objects, such as houses, schools, hospitals, and places of worship. In addition, there were reports of large-scale destruction and appropriation of property by all parties to the conflict, as well as forcible displacement of civilians on a broad scale.
Source.https://www.state.gov/